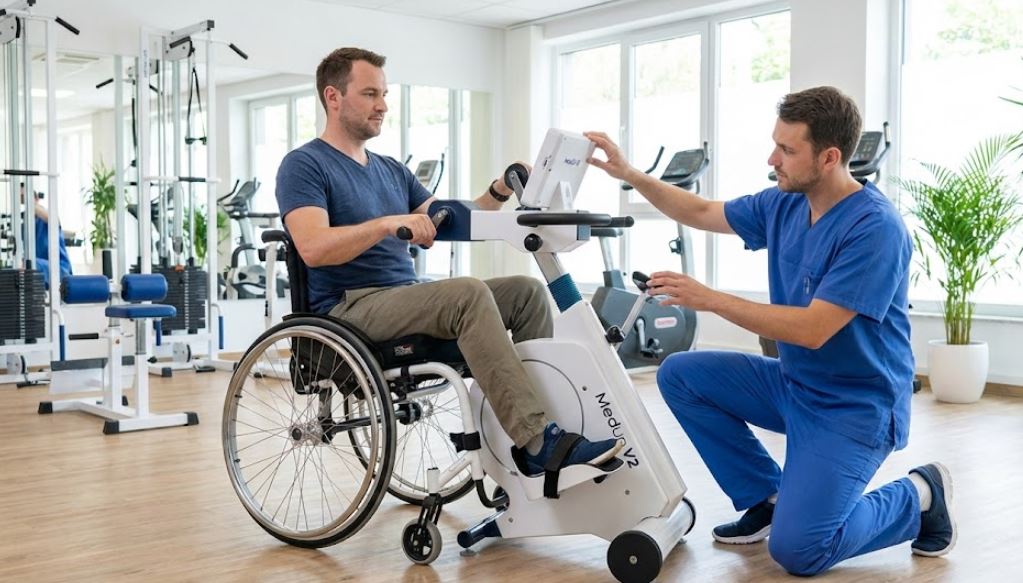
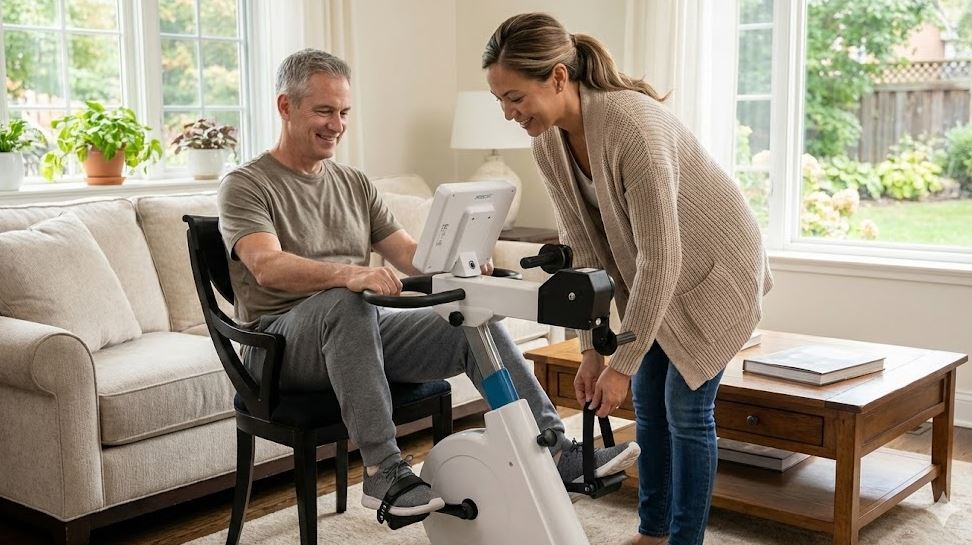
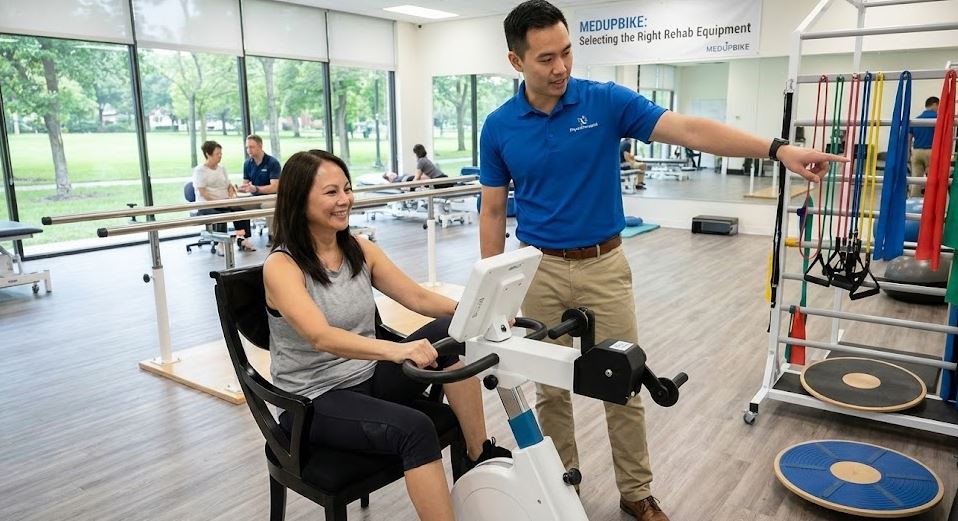
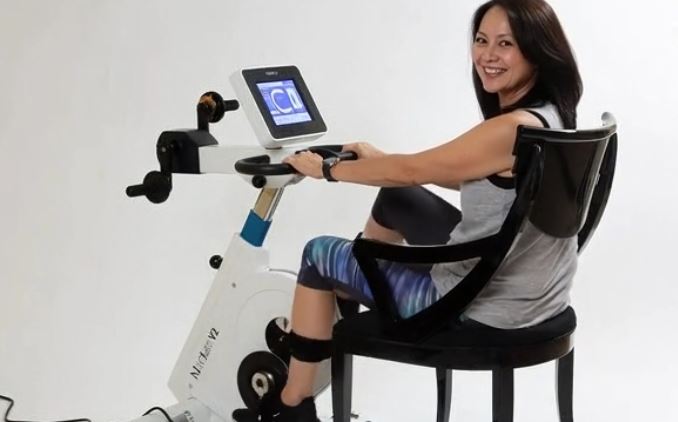
When conventional exercise equipment isn’t an option, many individuals with limited mobility or neuromuscular conditions struggle to stay active and maintain functional fitness. Fortunately, motor-assisted cycle therapy offers a safe, effective way to keep muscles moving, improve circulation, and support rehabilitation—even when voluntary effort is limited.
Did you know? The MedUp V2 Active-Passive Cycle Trainer is a wheelchair-accessible, motor-assisted ergometer designed to help individuals with mobility challenges build strength, improve joint mobility, and maintain cardiovascular health. Learn more about its features and benefits.
Who benefits most from motor-assisted cycle therapy?
Motor-assisted cycling is especially valuable for people facing physical limitations due to injury, chronic health conditions, or neurological disorders. These populations often cannot use traditional exercise equipment safely or comfortably but can still experience meaningful benefits through assisted movement.
Common groups who benefit include:
- Individuals living with stroke-related weakness who need safe, repetitive movement to regain control and muscle function.
- People with multiple sclerosis (MS) where fatigue, weakness, and spasticity make independent exercise difficult.
- Those affected by Parkinson’s disease, where rhythm and coordination challenges can make traditional exercise unsafe.
- Individuals with spinal cord injuries, who need support for circulation and muscle stimulation.
- Seniors or long-term care residents with limited mobility because of aging, chronic illness, or general deconditioning.
- People recovering from orthopedic injuries or surgery where controlled movement promotes healing without strain.
These conditions often involve muscle weakness, reduced coordination, or spasticity, which make traditional exercise or even simple walking challenging. Assisted cycling gives users a way to participate in activity that adapts to their capabilities and encourages progress.
How motor-assisted cycling works
Unlike traditional stationary bikes that rely entirely on the user’s strength, motor-assisted cycle trainers incorporate a motor to support movement when voluntary effort is limited. This makes cycling accessible even on weaker or less mobile days.
There are usually three main modes:
- Passive mode: The motor moves the pedals for the user, promoting circulation and joint mobility without effort.
- Assisted mode: The user contributes effort while the motor supports when needed, ideal for gradual strength building.
- Active mode: Users pedal under their own power with resistance adjusted for strength and endurance goals.
This adaptability is especially important for populations with variable strength or stamina, such as people with MS or post-stroke weakness.
Physical and clinical benefits of assisted cycling
Motor-assisted cycle therapy isn’t just about movement—it supports multiple aspects of physical wellness that are often compromised in people with mobility challenges.
Improved circulation and cardiovascular health
Limited mobility can slow blood flow and increase the risk of complications like edema or blood clots. Assisted cycling gently stimulates circulation, which supports tissue health and cardiovascular function even when voluntary exercise isn’t possible.
Reduced muscle stiffness and spasticity
Muscles that aren’t regularly used tend to tighten, leading to pain and limited range of motion. Cycling in passive or assisted modes helps reduce spasticity and relax tight muscles, making daily activities more comfortable.
Joint mobility and flexibility
Repetitive cycling movements help maintain or improve joint mobility—critical for individuals who otherwise spend long periods seated or inactive. These gentle, low-impact motions support range of motion without placing undue stress on joints.
Strength building and muscle activation
In assisted mode, the user contributes effort alongside the motor. This gradual activation promotes muscle strength and endurance over time, even for people who are just beginning rehabilitation or living with chronic conditions.
Benefits beyond the physical
Assisted cycling also supports mental and emotional well-being. Regular activity—especially when adapted to individual capabilities—can boost mood, reduce feelings of isolation, and increase confidence. When people feel physically engaged and supported, motivation and overall quality of life often improve as well.
Who should talk to a healthcare professional first?
People with complex conditions such as unstable heart disease, severe autonomic dysfunction, or certain types of uncontrolled spasticity should consult their healthcare provider before beginning any therapy. Motor-assisted cycling is generally safe, but professional guidance ensures that the training plan aligns with individual health needs and therapy goals.