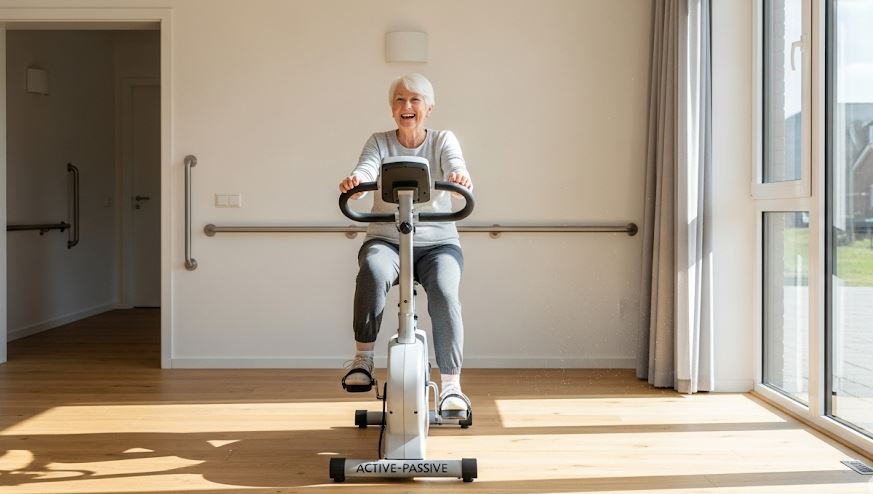
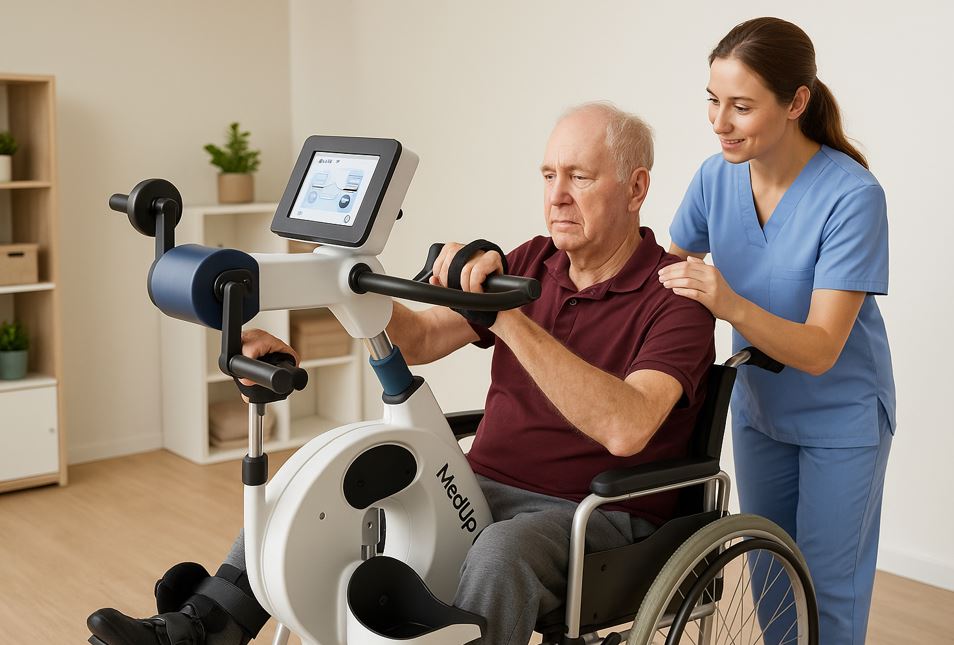
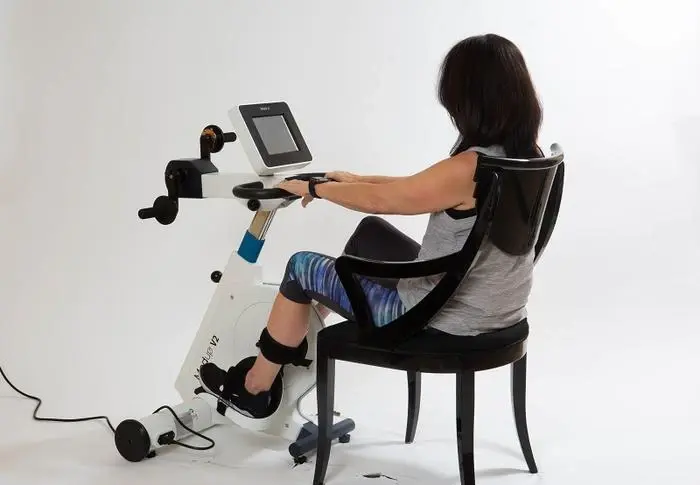
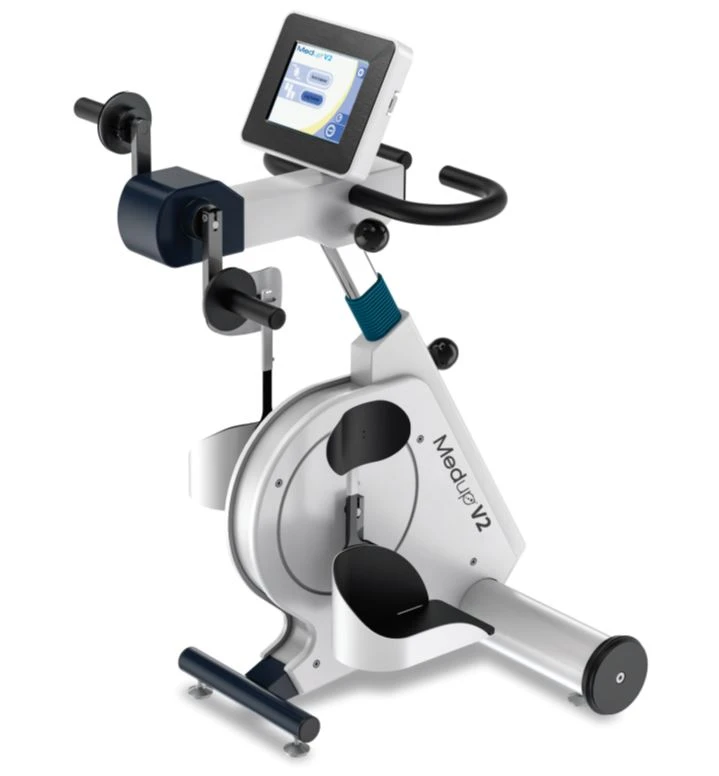
Maintaining mobility and overall health becomes more challenging as we age or face physical limitations. For many seniors and individuals with reduced mobility, traditional exercise can feel daunting—or even unsafe. This is where adaptive cycling, particularly using devices like the MedUp V2 active-Passive Cycle Trainer, can make a profound difference. By combining safety, ease of use, and therapeutic benefits, adaptive cycling offers a way to improve both physical and mental wellness without leaving home or requiring strenuous effort.
“Did you know? At MedUp, our Active-Passive Cycle Trainer helps seniors and people with limited mobility enjoy safe, effective exercise at home or in care facilities. Start improving your mobility and wellness today!”
The Physical Benefits of Adaptive Cycling
Adaptive cycling provides low-impact cardiovascular exercise that strengthens muscles, improves joint flexibility, and promotes better circulation. Unlike traditional stationary bikes, the Active-Passive Cycle Trainer allows users to pedal with assistance when needed, reducing strain while still promoting movement. This feature is especially helpful for seniors or individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries.
Research shows that even assisted cycling can:
- Enhance leg strength and core stability.
- Reduce stiffness and improve joint mobility.
- Support cardiovascular health, which is crucial for preventing chronic diseases such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
For healthcare facilities and long-term care homes, incorporating adaptive cycling into daily routines can help residents maintain independence and reduce the risk of falls. Programs that encourage consistent cycling—even for 10–15 minutes daily—can have measurable impacts on strength, endurance, and overall physical wellbeing. Learn more about exercise benefits for older adults.

Mental and Cognitive Benefits
Beyond physical improvements, adaptive cycling has notable mental health benefits. Exercise is linked to reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety, improved mood, and increased mental clarity. For seniors, especially those experiencing cognitive decline or conditions like dementia, cycling can stimulate brain function through repetitive, coordinated motion and engagement with the environment.
Active-Passive cycle trainers also promote social interaction when used in group settings, such as rehab sessions or senior activity programs. Even in solo sessions, the sense of accomplishment and autonomy can improve confidence and emotional wellbeing.
Safe and Accessible Exercise for Everyone
One of the main barriers to exercise among seniors and people with limited mobility is fear of injury. The design of adaptive bikes like MedUpBike’s Active-Passive Cycle Trainer addresses this concern. Features include:
- Stable, comfortable seating with secure support.
- Adjustable resistance levels and assisted pedaling.
- Compact designs suitable for home use or care facilities.
These features make it possible for users to gradually increase activity levels safely, avoiding overexertion while still gaining measurable benefits.
Integrating Adaptive Cycling into Daily Routines
For optimal results, adaptive cycling should become a regular part of a daily routine. Recommendations include:
- Short, consistent sessions of 10–20 minutes daily or several times per week.
- Gradual adjustments in resistance to improve strength and endurance over time.
- Incorporation of cognitive or social elements, such as music, conversation, or guided exercise programs, to maximize mental stimulation.
Caregivers and rehabilitation specialists can track progress easily, noting improvements in endurance, flexibility, and mood. Over time, these small, consistent efforts can translate into significant quality-of-life improvements.
Who Can Benefit Most?
Adaptive cycling is beneficial for:
- Seniors aiming to maintain or improve mobility.
- Individuals recovering from surgery or injury.
- People with limited mobility due to neurological conditions, arthritis, or other chronic illnesses.
- Rehabilitation and long-term care programs looking for safe, engaging exercise options.
MedUp V2’s solution bridges the gap between accessibility and therapeutic benefit, making it a practical addition to both personal and institutional wellness plans.
Why MedUpBike’s Active-Passive Cycle Trainer Stands Out
Unlike traditional exercise equipment, MedUpBike’s Active-Passive Cycle Trainer allows users to pedal independently or receive assistance, ensuring exercise is never too strenuous or unsafe. It’s durable, easy to maintain, and suitable for multiple users in healthcare settings. For families and caregivers, it provides peace of mind knowing their loved ones are exercising safely and effectively.
Adaptive cycling is more than just a workout—it’s a pathway to improved mobility, independence, and overall wellness. By integrating devices like the Active-Passive Cycle Trainer into daily routines, seniors and individuals with limited mobility can experience the physical, cognitive, and emotional benefits of consistent exercise.
Explore how MedUp V2 can help your loved ones or residents regain strength and wellness. Book a call or learn more today.