Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic illness that affects the central nervous system, leading to a wide range of physical and mobility challenges. For those living with MS, maintaining physical activity is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. The MedUp V2 Active Passive Cycle Trainer offers a unique solution, providing both active and passive exercise options that cater to varying levels of mobility and strength. In this post, we’ll explore the physical and mobility challenges faced by individuals with MS and how the MedUp V2 can make a positive impact.
Understanding MS and Its Challenges
MS is characterized by the immune system attacking the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. This can result in a variety of symptoms, including:
- Muscle Weakness: Reduced strength, particularly in the legs, making walking and other movements difficult.
- Spasticity: Stiffness and involuntary muscle spasms that can hinder mobility.
- Fatigue: A pervasive tiredness that can significantly limit physical activity.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Difficulty in maintaining balance, leading to an increased risk of falls.
- Pain and Sensory Problems: Numbness, tingling, and chronic pain that affect daily activities.
These challenges can make traditional forms of exercise daunting, but staying active is essential for managing MS symptoms and overall health.
The Role of Exercise in Managing MS
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with MS, including:
- Improved Muscle Strength and Function: Helps combat muscle weakness and spasticity.
- Enhanced Cardiovascular Health: Supports heart health and reduces fatigue.
- Better Balance and Coordination: Exercises that focus on balance can decrease the risk of falls.
- Mental Health Benefits: Physical activity can reduce depression and anxiety, common in those with MS.
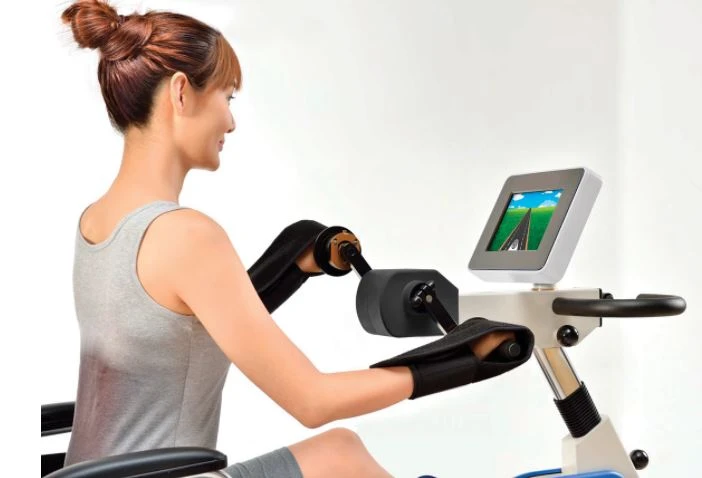
Introducing the MedUp V2 Active Passive Cycle Trainer

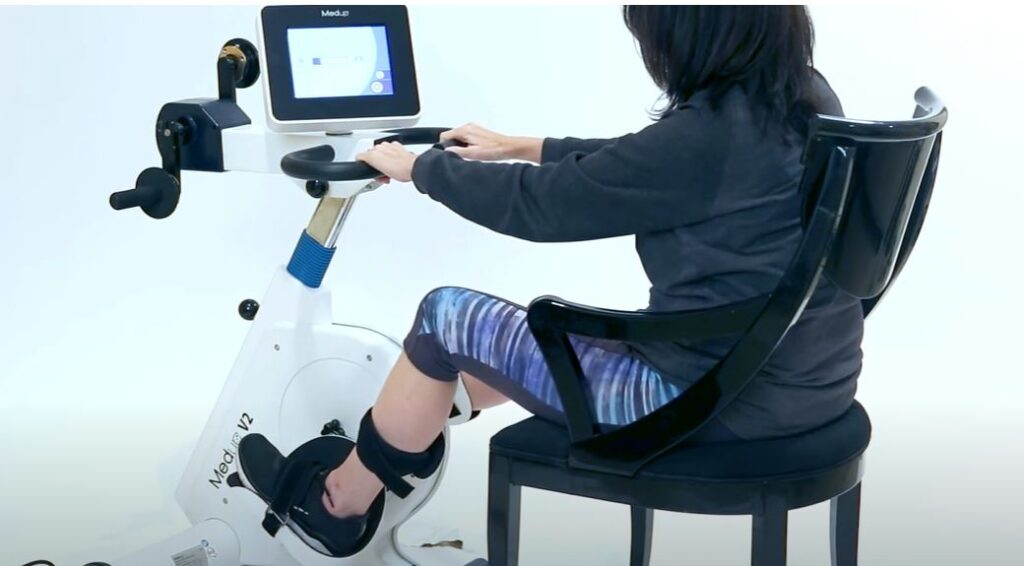
The MedUp V2 Active Passive Cycle Trainer is specifically designed to address the unique needs of individuals with limited mobility or strength, making it an excellent tool for those with MS. Here’s how it can help:
1. Dual-Mode Operation for Customized Exercise
- Active Mode: Allows users to pedal independently, promoting muscle strength and endurance. This mode is perfect for days when you feel more energetic and capable.
- Passive Mode: The motor assists in pedaling, providing gentle, low-impact exercise. This is ideal for days when fatigue or muscle weakness is more pronounced.
2. Adjustable Settings for Personalized Workouts
- Speed and Resistance Levels: Easily customize the workout intensity to match your current capabilities and gradually increase as your strength improves.
3. Low-Impact Exercise
- Joint-Friendly: The cycling motion is smooth and low-impact, reducing strain on joints and minimizing the risk of injury.
4. Compact and User-Friendly Design
- Ease of Use: The MedUp V2 is designed for simplicity, with an intuitive interface that makes tracking progress and adjusting settings straightforward.
- Convenience: Its compact size allows for use in various settings, from home to rehabilitation centers.
5. Therapeutic Benefits
- Circulation Improvement: Regular use can enhance blood flow, reducing numbness and improving overall limb health.
- Muscle Tone and Flexibility: Helps maintain and improve muscle tone and flexibility, essential for managing spasticity and muscle stiffness.
Real-Life Success Stories
Many individuals with MS have experienced significant improvements in their physical health and quality of life thanks to the MedUp V2. Here’s what some users have to say:
- “The MedUp V2 has been a lifeline for me. On days when my MS symptoms are too severe for a traditional workout, I can switch to passive mode and still get the exercise I need.” – Alex M.
- “Since incorporating the MedUp V2 into my routine, I’ve noticed a marked improvement in my muscle strength and a reduction in spasticity. It’s become an essential part of my daily life.” – Sarah T.
How to Get Started
Getting started with the MedUp V2 is easy:
- Set Up: Follow the simple instructions to assemble and set up your cycle trainer.
- Choose Your Mode: Select active or passive mode based on your daily needs.
- Customize Settings: Adjust the speed and resistance to your comfort level.
- Start Exercising: Enjoy the benefits of a tailored, low-impact workout.
Living with MS Can Be Better
Living with MS presents numerous challenges, but staying active is a powerful way to manage symptoms and enhance quality of life. The MedUp V2 Active Passive Cycle Trainer provides a versatile, user-friendly solution that adapts to your needs, whether you’re seeking a vigorous workout or a gentle, assisted exercise session. Embrace the benefits of low-impact cycling and take a proactive step towards better health with the MedUp V2.
Ready to experience the benefits of the MedUp V2? Transform your approach to managing MS and enjoy the freedom of movement and improved health.