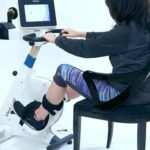
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that affects the peripheral nerves, causing weakness, numbness, and pain, typically in the hands and feet. While the primary symptoms are sensory and motor deficits, spasticity—an increase in muscle tone leading to stiffness and spasms—can also be a significant and debilitating symptom for many individuals. One innovative approach to managing spasticity in peripheral neuropathy is through the use of active-passive therapeutic cycle training. This blog will delve into the benefits of this therapeutic approach, how it works, and why it can be a game-changer for those suffering from peripheral neuropathy.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is often associated with underlying conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, infections, inherited disorders, or even exposure to toxins. The peripheral nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. When these nerves are damaged, it can result in a variety of symptoms including:
- Numbness and Tingling: A common initial symptom that can progress over time.
- Pain: Often described as burning, sharp, or stabbing.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness, particularly in the extremities.
- Coordination Issues: Difficulty in maintaining balance and coordination.
- Spasticity: Increased muscle tone leading to stiffness and involuntary muscle spasms.
The presence of spasticity can complicate the daily lives of individuals with peripheral neuropathy, making movement painful and challenging.
What is Active-Passive Therapeutic Cycle Training?
Active-passive therapeutic cycle training involves the use of a specially designed stationary bike that allows for both active (self-initiated) and passive (machine-assisted) movement. These bikes are equipped with motors that can assist in pedaling when the user’s muscle strength is insufficient or when spasticity restricts movement. This dual approach provides several therapeutic benefits:
- Active Mode: Encourages voluntary muscle activation, improving strength and coordination.
- Passive Mode: The motor assists in movement, reducing spasticity and preventing muscle atrophy.
Benefits of Active-Passive Therapeutic Cycling for Peripheral Neuropathy
The benefits of cycle therapy in peripheral neuropathy are wide ranging, including:
- Reduction in Spasticity
Spasticity can severely limit mobility and increase discomfort. Passive cycling helps to stretch and relax muscles, reducing the frequency and severity of spasms. Regular use can lead to long-term improvements in muscle tone and a significant reduction in spasticity.
- Improved Blood Circulation
Peripheral neuropathy often impairs blood flow, particularly in the extremities. Cycling, even in a passive mode, promotes better circulation, which can help reduce pain and improve overall limb health.
- Enhanced Muscle Strength and Coordination
In the active mode, therapeutic cycling encourages the use of muscles, enhancing strength and coordination. This is particularly beneficial for those experiencing muscle weakness as a result of peripheral neuropathy.
- Prevention of Muscle Atrophy
Muscle atrophy is a common issue for those with peripheral neuropathy, especially when spasticity limits movement. Passive cycling keeps muscles engaged and active, preventing atrophy and maintaining muscle mass.
- Pain Management
Regular exercise, including therapeutic cycling, has been shown to release endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers. This can help manage chronic pain associated with peripheral neuropathy.
- Improved Mental Health
The psychological benefits of exercise cannot be overstated. Engaging in regular physical activity can improve mood, reduce anxiety and depression, and enhance overall quality of life.
How to Incorporate Active-Passive Therapeutic Cycling into Your Routine
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any new exercise regimen, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions like peripheral neuropathy. They can provide guidance on the appropriate intensity and duration of exercise.
- Start Slowly
Begin with short sessions of passive cycling to allow your body to adjust. Gradually increase the duration and intensity as your strength and tolerance improve.
- Combine with Other Therapies
Therapeutic cycling should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes such as improved diet and stress management.
- Set Realistic Goals
Setting achievable goals can help keep you motivated. Track your progress and celebrate small milestones along the way.
- Stay Consistent
Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of therapeutic cycling. Aim for regular sessions, ideally several times a week, to see the best results.
Success Stories
Numerous individuals with peripheral neuropathy have reported significant improvements in their symptoms through the use of active-passive therapeutic cycle training. For instance:
- John’s Story: Diagnosed with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, John experienced severe foot pain and spasticity that limited his mobility. After incorporating therapeutic cycling into his routine, he noticed a marked reduction in spasms and an improvement in his ability to walk without pain.
- Mary’s Journey: Mary, who suffers from autoimmune-related neuropathy, found that regular sessions on the therapeutic cycle helped manage her pain and improved her overall energy levels. The passive mode was particularly beneficial on days when her symptoms were more pronounced.
A Path to Greater Wellness
Active-passive therapeutic cycle training offers a promising approach to managing spasticity and other symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. By combining the benefits of both active and passive movement, this innovative therapy can enhance muscle strength, improve circulation, reduce pain, and significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition. If you or a loved one are struggling with peripheral neuropathy, consider discussing the potential of therapeutic cycling with your healthcare provider to see if it could be a beneficial addition to your treatment plan.
By integrating therapeutic cycling into your routine, you can take an active role in managing your symptoms and improving your overall well-being. Remember, the journey to better health is a marathon, not a sprint, and every pedal stroke brings you one step closer to a more active and fulfilling life.